Orochem Technologies Inc.
Special Issues
High Throughput Sample Preparation Method for Drugs of Abuse in Urine
A simple, high throughput sample preparation method has been developed and validated for quantitation of over 40 drugs of abuse and metabolites using a polymeric SPE plate. Urine samples were hydrolyzed with E. Coli recombinant β-glucuronidase and then extracted with a Panthera Deluxe SPE plate. The eluates were separated using a Gazelle C18 UHPLC column and detected using an ExionLC-API4500 mass spectrometer. For most drugs, both the extraction and hydrolysis recoveries were over 90%.
In 2014, nearly two million Americans either abused or were dependent on prescription opioid pain relievers. Ninety one Americans die every day from an overdose involving either prescription opioids or heroin. Today's abuse profile combines both clinical and street drugs.
Drugs of abuse are commonly tested in clinical labs using the dilute and shoot approach, which comes with high matrix interference at low concentration and long-term deterioration of the LC–MS system. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the solid phase extraction approach as an alternative. Combining efficient hydrolysis based on E. Coli recombinant β-glucuronidase with an automated extraction method enables robust and dependable results.
Experimental
Materials
All drugs of abuse standards, their isotope internal standards (IS), codeine-6-β-D-glucuronidase, and morphine-3-β-D-glucuronidase were purchased from Cerilliant (MA, USA). BG100 β-glucuronidase was provided by Biotec-La Piedra Biotechnologia SpA (Chile). E. Coli β-glucuronidase (BG) was purchased from Campell Science (IL, USA). The Panthera Deluxe Polymeric SPE plate (30 mg/well), the Celerity Deluxe Polymeric SPE plate (30 mg/well), the Orpheus C18 SPE plate (50 mg/well), and the Gazelle C18 2.1 mm I.D. × 50 mm UHPLC column (1.7 µm) were manufactured by Orochem Technologies Inc. (IL, USA). The two polymeric SPE products A and B were manufactured by competitors.
Instrumentation
The ExionLC-API4500 Triple Quad MS (AB Sciex) was operated in negative ion mode for barbiturates and THCA and in positive ion mode for the rest of the drugs.
Orochem's EZYPRESS HT96-well plate positive pressure manifold unit was used for the SPE procedures. Evaporation was carried out using a Quikvap 96-well plate evaporator (Orochem Technologies Inc.).
Methods
Sample Preparation Procedures
Human urine samples were fortified with standards at different concentrations. For the enzyme hydrolysis recovery test, human urine samples were fortified with codeine-6-β-D-glucuronide, morphine-3-β-D-glucuronide, and 6-MAM at ULOQ level (equal to 2000 ng/mL free drug level) or with THCA-glucuronide at HQC level (equal to 200 ng/mL free drug).
Optimized SPE method for barbiturates and THCA: 0.1 mL of fortified urine was mixed with 0.05 mL of internal standard solution (IS) in 90% methanol solution, and 0.1 mL of pre-made mixture of 200 mM ammonium acetate pH 6.8 buffer and BG solution in 5/2 v/v ratio and incubated at 55 °C for 30 min. A Panthera Deluxe SPE plate (30 mg/well, 2 cc/well plate) was pre-conditioned with 1 mL of methanol followed by 1 mL of water. Hydrolyzed urine solution was loaded onto the extraction plate, which was then washed with 1 mL each of water and 20% methanol. The analytes were eluted with 1.5 mL of methanol. Solvent was evaporated under nitrogen at 45 °C and the analytes were then reconstituted with 0.5 mL of 30% methanol and injected into the LC–MS/MS.
SPE method for other drugs and metabolites: A mixture of 0.25 mL of master mix (ammonium acetate buffer, 25 µL of BG100 glucuronidase and IS) and 0.1 mL of fortified urine was incubated at 68 °C for 30 min. A Panthera Deluxe SPE plate (30 mg/well, 2 cc/well plate) was pre-conditioned with 1 mL of methanol and then 1 mL of water. Hydrolyzed urine solution was loaded onto the extraction plate and then washed with 1 mL each of water and 5% methanol. The analytes were eluted with 1.0 mL of methanol and evaporated under nitrogen at 40 °C and then reconstituted with 0.3 mL of 5% methanol and injected into the LC–MS/MS.
UHPLC–MS/MS Conditions
A Gazelle C18 (1.7 µm), 2.1 mm I.D. × 50 mm long UHPLC column was used for the separation. For the barbiturates and THCA, the gradient mobile phase was composed of 0.1% formic acid in water (A) and 0.1% formic acid in methanol (B). The gradient ran from 30% to 95% B. The rest of the compounds used a gradient mobile phase of 0.1% formic acid in water containing 20 mM of an ammonium buffer (A) and 0.1% formic acid in methanol (B). The gradient ran from 5% to 95% B.
An ExionLC-API4500 Triple Quad MS (AB Sciex) was operated in negative ion mode for barbiturates and THCA and in positive ion mode for rest of the drugs.
Results
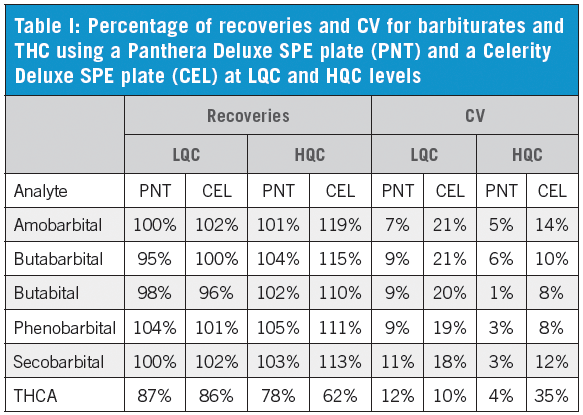
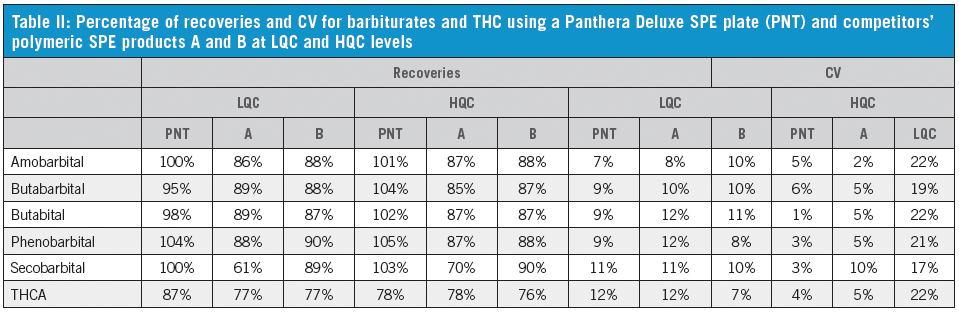
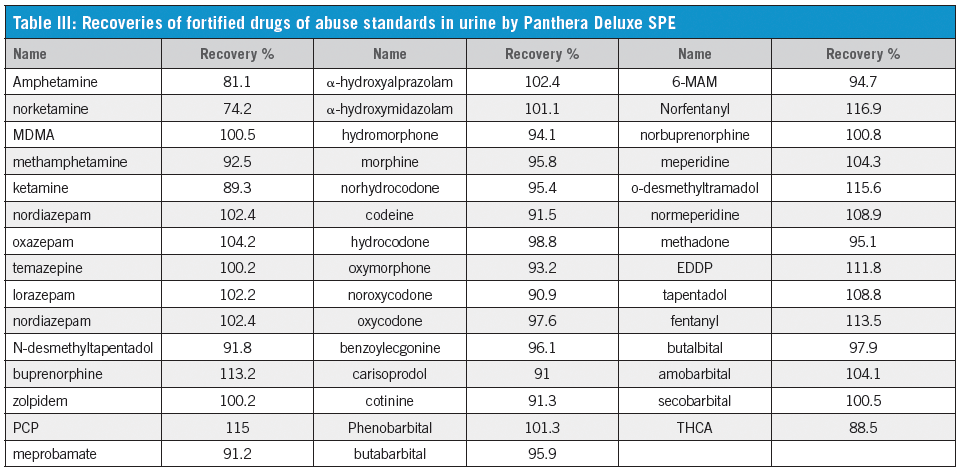
We have established that the Panthera Deluxe SPE plate gives better reproducibility and recovery than the Celerity Deluxe Plate, especially for THCA (Table I). It also shows better performance than the two competitor polymeric SPE products (Table II). The C18 plate gives poor recoveries for most compounds. The extraction recoveries were in the range of 74.2–116.9% for all drugs (Table III).
Under current hydrolysis conditions, recoveries of codeine-6-β-glucuronide and morphine-3-β-glucuronide were 89.9% and 110.5%, respectively, while the recovery of labile analyte 6-MAM was 100.8%. Recovery of THCA-glucuronide was 89.5%.
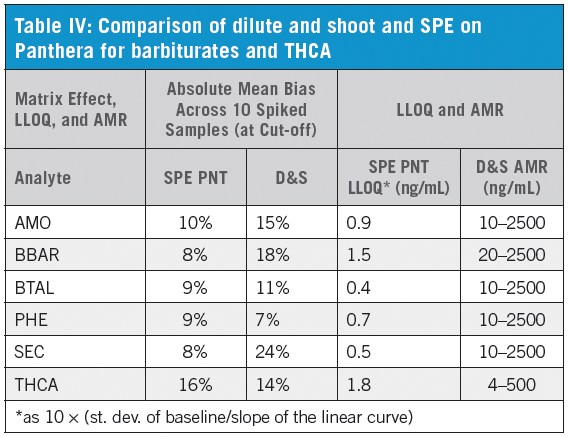
Compared to dilute and shoot (D&S), the Panthera Deluxe procedure gave overall better results demonstrating greater AMR and lower LLOQ (Table IV). Results for xenobiotic interference/effect testing and matrix induced ion suppression/enhancement were comparable between procedures, while Panthera SPE showed superior results in terms of matrix interference/effect tested at cut-off concentration. Response factors for barbiturates and THCA clearly improved with SPE (Figure 1).
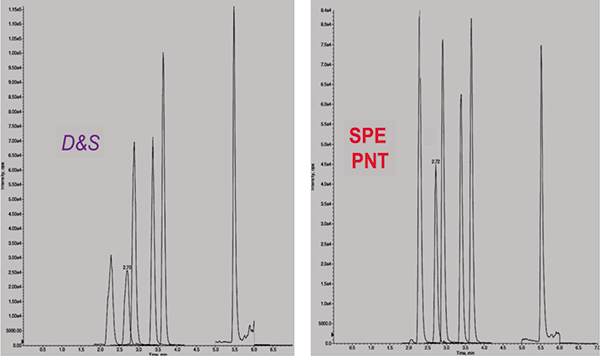
Figure 1: Mass chromatograms of fortified urine (at cut-off) processed by dilute and shoot (left) and the Panthera SPE process (right). Peaks in eluting order: phenobarbital, butabarbital, butalbital, amobarbital, secobarbital, and THCA.
Several different mobile phases were tested. For most of the compounds, there was no significant difference in peak shapes with or without ammonium buffer; however, ammonium buffer did significantly improve benzodiazine's peak shapes. There was no significant fronting or tailing of the opiates using the Gazelle C18 UHPLC column (Figure 2).
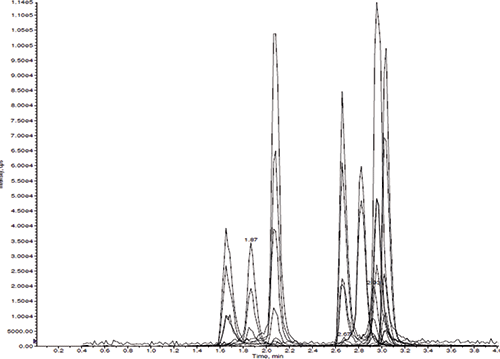
Figure 2: Mass chromatograms of morphine, oxymorphone, hydromorphone, codeine, oxycodone, noroxycodone, hydrocodone, norhydrocodone, and 6-MAM (peak from left to right) in fortified urine sample using the Panthera Deluxe SPE process.
Conclusion
Orochem has developed fast and reliable SPE methods for the analysis of over 40 drugs of abuse in a urine toxicology setting. These improved methods demonstrate reduced matrix effects and expand the lower end of the AMR by almost an order of magnitude. The sample processing time per plate is about 15 min and the total cost of sample preparation is maintained at a very competitive level. Furthermore, Panthera SPE demonstrates improved performance over its predecessor, Celerity, and over two other major competitor products.
Orochem Technologies Inc.
340 Shuman Blvd., Naperville, IL 60563
tel. (630) 210-8300
Website: www.orochem.com

A Novel LC–QTOF-MS DIA Method for Pesticide Quantification and Screening in Agricultural Waters
May 8th 2025Scientists from the University of Santiago de Compostela developed a liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC–QTOF-MS) operated in data-independent acquisition (DIA) mode for pesticide quantification in agriculturally impacted waters.
Investigating 3D-Printable Stationary Phases in Liquid Chromatography
May 7th 20253D printing technology has potential in chromatography, but a major challenge is developing materials with both high porosity and robust mechanical properties. Recently, scientists compared the separation performances of eight different 3D printable stationary phases.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)







