Metal-Free Columns Significantly Improve Peak Shape, Recovery, and Sensitivity for Phosphorylated Compounds
LCGC North America
Phosphorylated compounds readily adsorb to stainless steel surfaces present within the flow path of an HPLC system. This process can lead to poor peak shape, low recovery of sample, and reduction in sensitivity. Here we show that our metal-free column housing technology can improve analysis of these compounds.
HPLC columns are commonly made with stainless steel 316, which is a combination of iron, carbon, manganese, and silicon, with high amounts of nickel, chromium, and molybdenum. The corrosion resistance of stainless steel is caused by the formation of a passive layer of chromium and nickel oxides on the surface, which prevent penetration of corrosive elements. These oxide layers have a high affinity to phosphorylated compounds, particularly those that have accessible phosphate groups.
An illustration of this interaction is shown in Figure 1. As the analyte band travels through the column, it will lose sample through adsorption to the metal surface, resulting in low recovery and a reduction in sensitivity. Adsorption also interferes with uniform sample flow causing peak tailing which can be observed in the resulting chromatogram.
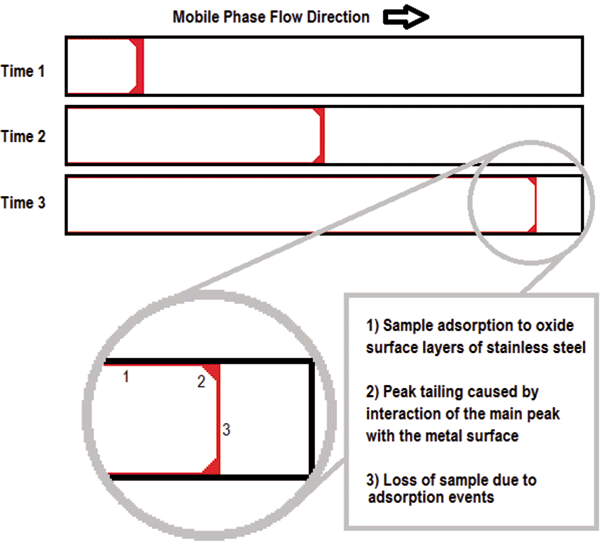
Figure 1: A simplified schematic diagram of analyte loss caused by adsorption of phosphorylated compounds to stainless steel HPLC column housing.
We recently developed metal-free housing to prevent such unwanted interactions. Our design utilizes stainless steel hardware, in order to preserve high pressure capabilities, with internal PEEK coatings (tubing, end fittings, inlet and outlet frits). This removes the largest contribution of metal surfaces within the HPLC sample flow path.
Experimental Conditions
Figure 2 shows several triphosphates under identical conditions in both stainless steel and metal-free housings.
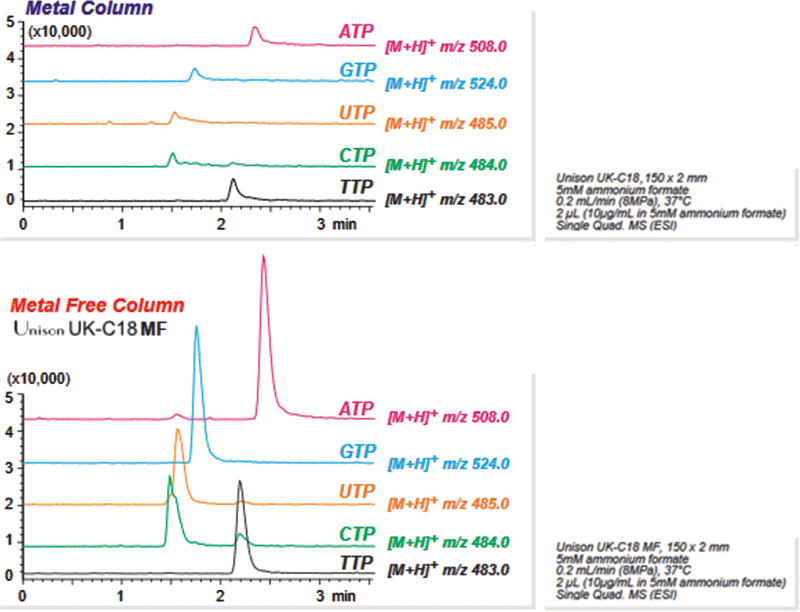
Figure 2: Triphosphates on stainless steel versus metal-free columns.
Result and Discussion
All triphosphates tested show evidence of adsorption and poor peak shapes with a metal column, which is not seen on our metal-free column. Marked improvements in peak shape and sample recovery, were observed as evidenced by the noticeably larger area under each curve.
Conclusion
When troubleshooting issues with poor peak shape and recovery, contributions of interaction with the column housing are often overlooked. Here we show that there can be considerable interaction of certain analytes with metal surfaces within the column, which can be remedied with the use of a metal-free column. We propose that in any trouble shooting scenario where peak shape cannot be improved through modification of the mobile phase, the use of a metal-free column should be considered.

Imtakt USA
2892 NW Upshur St., Portland, OR 97210
tel. (888) 456-HPLC, (215) 665-8902, fax, (501) 646-3497
Website: www.ImtaktUSA.com

Free Poster: NDSRI Risk Assessment and Trace-Level Analysis of N-Nitrosamines
April 25th 2025With increasing concern over genotoxic nitrosamine contaminants, regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have introduced strict guidelines following several high-profile drug recalls. This poster showcases a case study where LGC and Waters developed a UPLC/MS/MS method for quantifying trace levels of N-nitroso-sertraline in sertraline using Waters mass spectrometry and LGC reference standards.
New TRC Facility Accelerates Innovation and Delivery
April 25th 2025We’ve expanded our capabilities with a state-of-the-art, 200,000 sq ft TRC facility in Toronto, completed in 2024 and staffed by over 100 PhD- and MSc-level scientists. This investment enables the development of more innovative compounds, a broader catalogue and custom offering, and streamlined operations for faster delivery. • Our extensive range of over 100,000 high-quality research chemicals—including APIs, metabolites, and impurities in both native and stable isotope-labelled forms—provides essential tools for uncovering molecular disease mechanisms and exploring new opportunities for therapeutic intervention.
New Guide: Characterising Impurity Standards – What Defines “Good Enough?”
April 25th 2025Impurity reference standards (IRSs) are essential for accurately identifying and quantifying impurities in pharmaceutical development and manufacturing. Yet, with limited regulatory guidance on how much characterisation is truly required for different applications, selecting the right standard can be challenging. To help, LGC has developed a new interactive multimedia guide, packed with expert insights to support your decision-making and give you greater confidence when choosing the right IRS for your specific needs.
Using the Carcinogenic Potency Categorisation Approach (CPCA) to Classify N-nitrosamine Impurities
April 25th 2025Learn how to manage nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals with our free infographic. Discover how the CPCA approach establishes acceptable intake limits and guides the selection of NDSRI reference samples. Stay compliant and ensure safety with our ISO-accredited standards.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)








