Evaluation of Automated Solid-Phase Extraction for Nitrosamines Using US EPA Method 521
Special Issues
Disinfection by-products (DBP) are an ever-present nuisance in the efforts to purify drinking water, wastewater, and municipal waters from various sources. An emerging class of DBP compounds with health effects is nitrosamines which result from chloramination or chlorination if the water is nitrogen-rich. Five of these nitrosamines have been listed on the US EPA’s new Contaminant Candidate List (CCL-3). Of the nitrosamines, the most common and problematic is N-nitrosdimethylamine (NDMA). The maximum admissible levels set by the US EPA are 7 ng/L for NDMA and 2 ng/L for N-nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA).
Disinfection by-products (DBP) are an ever-present nuisance in the efforts to purify drinking water, wastewater, and municipal waters from various sources. An emerging class of DBP compounds with health effects is nitrosamines which result from chloramination or chlorination if the water is nitrogen-rich. Five of these nitrosamines have been listed on the US EPA’s new Contaminant Candidate List (CCL-3). Of the nitrosamines, the most common and problematic is N-nitrosdimethylamine (NDMA). The maximum admissible levels set by the US EPA are 7 ng/L for NDMA and 2 ng/L for N-nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA).
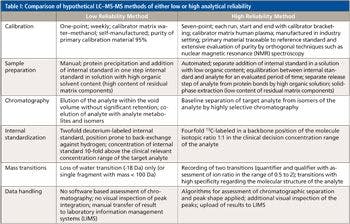
The US EPA developed method 521 to measure seven nitrosamines in drinking water using solid phase extraction (SPE) and GC-MS-MS with large volume injection and chemical ionization for sensitive analysis. Sample preparation for EPA 521 involves passing 0.5 L of sample water through 6-mL coconut charcoal SPE cartridges. Nitrosamines are then eluted with methylene chloride and further concentrated to 1 mL. Analysis is then performed with tandem mass spectrometry after gas chromatography separation (GC-MS-MS). A large volume injection (LVI) of 8 µL onto the GC column is used to increase sensitivity. Chemical ionization (CI) is used to preserve the molecular ion with minimal adducts. An ion trap or triple quadrupole MS is used for MS-MS. The purpose of this application note is to demonstrate that in addition to modern measurement technology the addition of automated solid phase extraction can improve method performance (1).
Results and Discussion
The chromatography is shown in Figure 1 and shows excellent separation of the desired compounds in a 12-min run, shortened from the suggested separation methods of 32 and 42.5-min in Method 521.
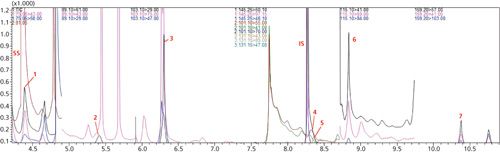
Figure 1: 5-ng/L standard with internal standard and surrogate added. Zoom used to show the detail of peaks. 1. NDMA, 2. NMEA, 3. NDEA, 4. NPYR, 5. NDPA, 6. NPIP, 7. NDBA, SS NDMA-d6, IS NDPA-d14.
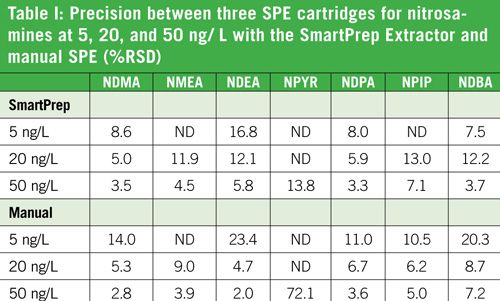
Precision of the SmartPrep® Extractor and manual SPE were compared by extracting three concentrations, 5, 20, and 50 ng/ mL, with three cartridges each and is shown in Table I. It can be seen that precision between three replicates is better for the automated system rather than the manual system. Although the method very specifically mentions care in not letting the cartridge go dry once the process is started, it is difficult in a multi-step process to be as reproducible as an automated system.
References
(1) D.D. Carlton Jr. and K.A. Schug, “Evaluation of Automated Solid-Phase Extraction for Nitrosamines Using US EPA Method 521,” AN1001504_01, www.horizontechinc.com (2015).

Horizon Technology, Inc.
16 Northwestern Drive, Salem, NH 03079
tel. (603) 893-3663
Website: www.horizontechinc.com

Separation of Ultra-Short and Long Chain PFAS Compounds Using a Positive Charge Surface Column
December 11th 2024A separation of ultra-short and long chain PFAS (C1-C18) is performed on a HALO®PCS Phenyl-Hexyl column along with a HALO®PFAS Delay column which demonstrates excellent retention for both hydrophilic and hydrophobic analytes.