Determination of Ephedra Alkaloids and Synephrine in Dietary Supplements via Strong Cation‑Exchange SPE and LC–MS/MS Detection
The Application Notebook
Ephedra alkaloids are phenethylamines that occur naturally in plants, including the herb Ma Huang used in traditional Chinese medicine. Ephedra alkaloids are potent CNS stimulants and also have a sympathomimetic effect on the peripheral nervous system. The aim of this study was to develop a multi-analyte procedure for the extraction, cleanup, and quantification of the ephedra alkaloids in functional foods and natural products. High capacity strong cation-exchange SPE cartridges were used for the isolation of ephedrine, pseudoephedrine, norephedrine, norpsuedoephedrine, methylephedrine, and synephrine from dietary supplements.
Brian Kinsella, UCT, LLC
Ephedra alkaloids are phenethylamines that occur naturally in plants, including the herb Ma Huang used in traditional Chinese medicine. Ephedra alkaloids are potent CNS stimulants and also have a sympathomimetic effect on the peripheral nervous system. The aim of this study was to develop a multi-analyte procedure for the extraction, cleanup, and quantification of the ephedra alkaloids in functional foods and natural products. High capacity strong cation-exchange SPE cartridges were used for the isolation of ephedrine, pseudoephedrine, norephedrine, norpsuedoephedrine, methylephedrine, and synephrine from dietary supplements.
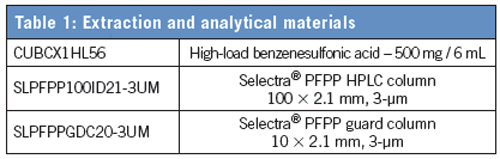
Procedure
1. Sample Pretreatment
a) Weigh 1 ± 0.1g of dietary supplement into a 15 mL polypropylene centrifuge tube. For this study, a SPEX® SamplePrep®GenoGrinder® was used to pulverize the tablets.
b) Add 10 mL of 1% formic acid to each sample.
c) Shake or vortex sample for 15 min to fully extract the ephedra alkaloids. Ensure samples are fully dissolved.
d) Centrifuge the sample for 10 min at ≥3000 × g and 4 °C.
2. SPE Procedure
SPE Conditioning
a) Add 2 × 4 mL of methanol to CUBCX1HL56 SPE cartridge.
b) Add 4 mL of ultrapure water.
c) Add 4 mL of 1% formic acid.
Note: Do not let the cartridge go dry otherwise repeat steps a) through c).
Sample Extraction
a) Load supernatant from step 1.
b) Allow sample to percolate through the cartridge or apply a vacuum if necessary (adjust vacuum for flow of 1–3 mL per minute).
Wash Cartridge
a) Add 2 × 4 mL of 0.1% formic acid.
b) Add 2 × 4 mL methanol.
c) Dry under vacuum for ≈30 s to remove excess solvent.
Elution
a) Elute the ephedra alkaloids using 8 mL of methanol containing 2% ammonium hydroxide.
b) Evaporate off the methanol solvent at 40 °C under a gentle stream of nitrogen until it reaches a volume of ≈1 mL.
c) Add 1 mL of aqueous mobile phase (10 mM ammonium acetate)
d) Evaporate off any remaining methanol*
e) Vortex the samples for 1 min and filter through a 0.2 µM syringe filter directly into a HPLC vial.
*Ephedra alkaloids are similar to amphetamines, which are known to be volatile compounds. Therefore, extra care was taken during the evaporation step to avoid any potential loss in recovery that may occur during this step.
Results
Figure 1: Chromatogram of a 10 ng/mL standard.
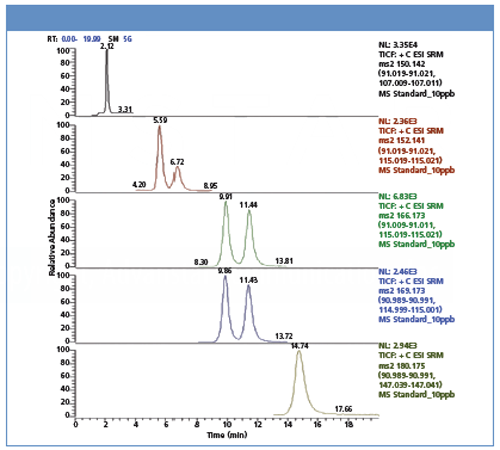
Conclusion
A method was successfully developed for the extraction, cleanup, and quantification of the ephedra alkaloids and synephrine in functional foods and natural products. Strong cation-exchange SPE was used to isolate the phenethylamines from the complex sample matrix, which consisted of nine herbal extracts containing a high concentration of calcium, caffeine, and additional excipients. A high capacity SPE sorbent was used because it offers better retention than standard SCX sorbent.

UCT, LLC
2731 Bartram Road, Bristol, Pennsylvania 19007, USA
Tel: (800) 385 3153
E-mail: methods@unitedchem.com Website: www.unitedchem.com

Regulatory Deadlines and Supply Chain Challenges Take Center Stage in Nitrosamine Discussion
April 10th 2025During an LCGC International peer exchange, Aloka Srinivasan, Mayank Bhanti, and Amber Burch discussed the regulatory deadlines and supply chain challenges that come with nitrosamine analysis.











