Detection of Aflatoxins in Milk at Picogram Levels Using SPE and LC–MS–MS
The Application Notebook
Aflatoxins (B1, B2, G1, and G2) are naturally occurring mycotoxins produced by fungi on agricultural crops. They are classified as carcinogenic and can pose a significant risk to human health if consumed. Although aflatoxin B1 is the most potent carcinogen, the main concern in milk is its hydroxylated metabolite, aflatoxin M1. To ensure the safety of milk, the US FDA established a tolerance of 0.5 µg/kg for aflatoxin M1 in milk, while the EU set a limit of 0.05 µg/kg in raw milk and 0.025 µg/kg in infant formula. A simple and effective method using polymeric solid-phase extaction (SPE) and liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS–MS) is presented for the analysis of aflatoxins in milk at the low concentrations required.
Aflatoxins (B1, B2, G1, and G2) are naturally occurring mycotoxins produced by fungi on agricultural crops. They are classified as carcinogenic and can pose a significant risk to human health if consumed. Although aflatoxin B1 is the most potent carcinogen, the main concern in milk is its hydroxylated metabolite, aflatoxin M1. To ensure the safety of milk, the US FDA established a tolerance of 0.5 µg/kg for aflatoxin M1 in milk, while the EU set a limit of 0.05 µg/kg in raw milk and 0.025 µg/kg in infant formula. A simple and effective method using polymeric solid-phase extaction (SPE) and liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS–MS) is presented for the analysis of aflatoxins in milk at the low concentrations required.
Sample Preparation
1. Sample Extraction 1 (aqueous)
Whole milk (20 g) was deproteinized with glacial acetic acid (200 µL),vortexed (5 min), and centrifuged (≥ 3000 g, 5 min).
2. SPE Extraction
SPE cartridges were conditioned with methanol (3 mL) and DI water (3 mL) prior to loading of the sample supernatant (≤ 5 mL/min).
3. Sample Extraction 2 (solvent)
The residual milk solids were extracted with acetone (10 mL). After centrifugation (≥ 3000 g, 5 min), the supernatant was transferred to a polypropylene centrifuge tube and the acetone removed by evaporation (50 °C, N2). The sample was dissolved in DI water (10 mL) and then applied to the same SPE cartridge used in step 2.
4. Wash Cartridge
The SPE cartridge was washed with DI water (3 mL), 50% methanol (3 mL) and dried under vacuum (≥10 inHg) for 10 min. The SPE cartridge was then washed with hexane (3 mL) and dried under vacuum (≥10 inHg) for 2 min.
5. Elution
The aflatoxins were eluted with acetone (4 mL), evaporated to dryness (50 °C, N2) and reconstituted in 1 mL of 50% methanol. Finally, the extracts were filtered with a 0.22-µm nylon syringe filter into an autosampler vial.
Analysis
Samples were analyzed on a Thermo ScientificTM DionexTM UltimateTM 3000 HPLC system coupled to a TSQ VantageTM triple quadrupole MS operated in ESI+ mode. The analytical column was a UCT Selectra C18. Samples were run using a gradient mobile phase of acidified water and acidified methanol.
Figure 1: Chromatogram of extracted milk sample at 0.5 µg/kg.
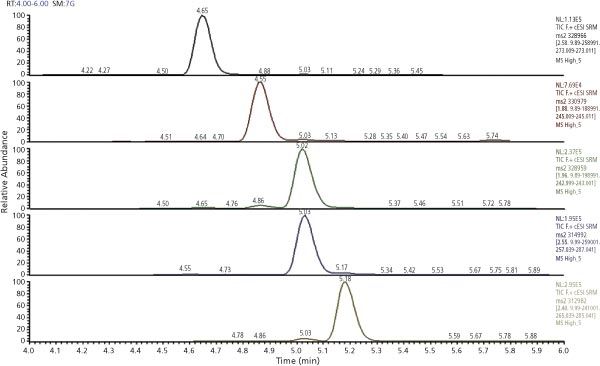
Results
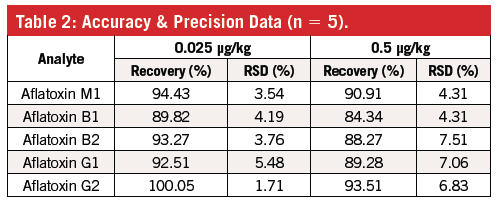
Conclusions
Whole milk was spiked at two concentration levels (0.025 and 0.5 µg/kg). Matrix-matched calibration curves (0.01–2 µg/kg) were used for quantitation. Linearity was ≥ 0.995. Excellent recovery (84–100%) and repeatability (< 8%) were obtained using the presented method. Extraction with an organic solvent was found to be necessary to obtain good extraction efficiency for the aflatoxins.

UCT, LLC
2731 Bartram Road, Bristol, PA 19007, USA
Tel: (800) 385-3153 Email: methods@unitedchem.com
Website: www.unitedchem.com

Accelerating Monoclonal Antibody Quality Control: The Role of LC–MS in Upstream Bioprocessing
This study highlights the promising potential of LC–MS as a powerful tool for mAb quality control within the context of upstream processing.
Using GC-MS to Measure Improvement Efforts to TNT-Contaminated Soil
April 29th 2025Researchers developing a plant microbial consortium that can repair in-situ high concentration TNT (1434 mg/kg) contaminated soil, as well as overcome the limitations of previous studies that only focused on simulated pollution, used untargeted metabolone gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to measure their success.
Prioritizing Non-Target Screening in LC–HRMS Environmental Sample Analysis
April 28th 2025When analyzing samples using liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry, there are various ways the processes can be improved. Researchers created new methods for prioritizing these strategies.
Potential Obstacles in Chromatographic Analyses Distinguishing Marijuana from Hemp
April 28th 2025LCGC International's April series for National Cannabis Awareness Month concludes with a discussion with Walter B. Wilson from the National Institute of Standard and Technology’s (NIST’s) Chemical Sciences Division regarding recent research his team conducted investigating chromatographic interferences that can potentially inflate the levels of Δ9-THC in Cannabis sativa plant samples, and possible solutions to avoid this problem.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)
















