Latest from LCGC International
5 days ago
Deep In The Heart of Texas: Pittcon 2026Latest Content

LC–MS Determination of PFAS Distribution in Porcine Tissues for Food Safety Monitoring

Chromatographic Characterization and Anticancer Activity of Scorpio fuscus Venom in Colorectal Cancer Models

Waters Completes Combination with BD Biosciences and Diagnostic Solutions Businesses

Chromatography-Based Metabolomic Insights for Safer Kimchi Fermentation

Volatile Organic Compound Profiling of Commercial Kombucha Using GC-TOF-MS and GC×GC-TOF-MS

Shorts










Podcasts
Videos
All Content
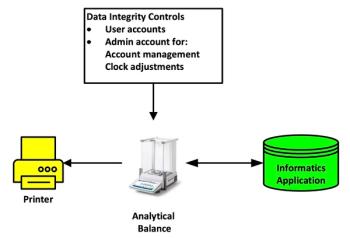
A new version of United States Pharmacopeia (USP) <41> Balances becomes effective in February 2026. This installment of “Questions of Quality” explores the impact of the changes this brings, along with developments in the Japanese and European Pharmacopoeias.

University of Erlangen–Nuremberg researchers applied a bottom-up proteomics workflow centered on microflow liquid chromatography (microLC) coupled to ion mobility quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (QTOF-MS) to authenticate walnut products and detect adulteration with cashew, hazelnut, and peanut.

Top articles published this week highlight troubleshooting issues close to the point of sample injection and the importance of continued collaboration between industry and academia.

The Pittsburgh Conference on Analytical Chemistry and Applied Spectroscopy (Pittcon) has served as a major international meeting for analytical scientists across academia, industry, and government laboratories for more than 75 years. Pittcon 2026 will take place March 7–11, 2026, at the Henry B. González Convention Center in San Antonio, Texas, under the conference theme The Scientific Frontier.

A liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) method for the determination of 39 emerging contaminants in water at ultra trace concentrations has been developed and validated.
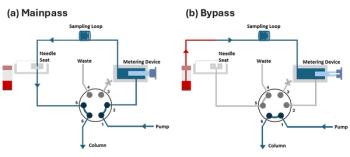
In this installment of “LC Troubleshooting,” we take a close look at how the commonly used “flow-through needle” sampler works, discuss how and where leaks can develop, and solutions to the problems when they do occur.
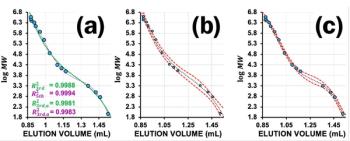
Bob Pirok discusses the use of R², adjusted R², and F-tests to pick the right SEC calibration curve polynomial to avoid overfitting.

Researchers compared leaf and in vitro callus extracts of Eucalyptus camaldulensis using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) to assess phytochemical composition and bioactivity. Callus extracts contained a greater diversity and higher abundance of secondary metabolites, including flavonoids and key volatiles such as 1,8-cineole, α-terpineol, and sabinene. Bioassays showed superior anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity in callus-derived oils, surpassing standard drugs, highlighting tissue culture as a powerful tool for enhancing natural therapeutic compounds.

LCGC International salutes Jack Henion and Bob W.J. Pirok, winners of the 19th annual LCGC Lifetime Achievement and Emerging Leader in Chromatography Awards, respectively.

Collaboration between academia and industry can reap rewards that cannot be achieved separately.

Malaria causes nearly one million deaths annually, prompting the search for new vector-control strategies. Inspired by chimpanzee behavior in Uganda’s Kibale National Park, researchers analyzed essential oils from four local tree species—three used for chimpanzee nesting—using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC–MS). A mixture of key compounds showed toxic and irritant effects on malaria-carrying mosquitoes, suggesting chimpanzee-inspired, plant-based repellents as a sustainable approach to the prevention of the disease.
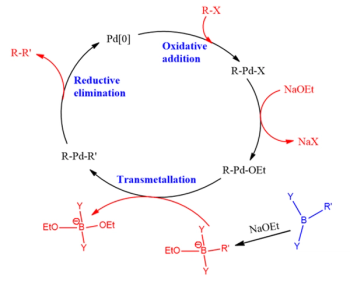
A quality attribute of Suzuki-Miyura coupling reactions is to measure residual levels of phosphine ligands in the reaction product. Residual phosphine ligands can be present in non-oxidized and oxidized forms. The non-oxidized and oxidized forms have different UV chromophores and can have differing solubility. These differences can preclude accurate and precise quantification. The extent of oxidation is difficult to prevent and control for calibration standards and test materials. This paper describes a method for derivatizing residual phosphines to the oxidized form. The oxidized form is stable and provides a basis for accurate quantification of residual phosphines. This overcomes the challenges for quantifying the non-oxidized and oxidized forms.

Headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (SPME) GC–MS was used by researchers to analyze concrete samples from a Michigan City basement after a 2022 confession to a 2017 murder in which the body was never recovered. The analysis detected multiple volatile organic compounds (VOCs) associated with human decomposition, indicating a body had decomposed in the room for an extended period. This study marked the first successful legal use of VOC evidence from concrete in Indiana and helped support the suspect’s conviction.

Combining silicon micro-nanofabrication technology to create perfectly ordered separation beds on a silicon chip, such as micro-pillar array columns (µPACs), is a powerful innovation in liquid chromatography. This article discusses the numerous possibilities of micro-nanofabrication in the future of analytical chemistry in life science, covering sample preparation, separation science, and detection technologies.
A recent review article highlights evolving MS-based methodologies that are reshaping ligand discovery and mechanistic characterization for membrane protein drug targets. LCGC International spoke to Andrew Reiter and Dina Schuster, two of the authors of the article, about these methodologies.