A Reliable and Routine GC/MS/MS Method for the Determination of Dioxins in Foodstuffs and Animal Feed
Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDD) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDF) are fat-soluble, highly toxic, ubiquitous environmental contaminants found at trace levels in all foodstuffs and animal feed.
INTRODUCTION
Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDD) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDF) are fat-soluble, highly toxic, ubiquitous environmental contaminants found at trace levels in all foodstuffs and animal feed. Current legislation in the European Union (EU) and the United States requires the confi rmation of PCDD and PCDF congeners by GC-high resolution mass spectrometry (GC-HRMS). In the event of a food-related dioxin contamination incident, many samples must be analyzed in as short a time as possible in order to determine the extent of the contamination and the subsequent potential risk to human health.
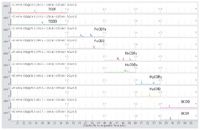
Figure 1. Chromatographic separation of native PCDD and PCDF congeners*
Agilent Technologies has partnered with a leading European dioxin laboratory to develop a method based on GC/MS/MS for the trace analysis of PCDD and PCDF congeners in foodstuffs and animal feed. The method provides sensitive and reproducible results that are comparable to those obtained by GC-HRMS. The GC/MS/MS method meets the requirements of current EU legislation for the screening of PCDD and PCDF congeners in foodstuffs and animal feed, and has potential as an alternative confirmatory methodology for the determination of PCDD and PCDF congeners in offi cial food and feed control, pending analytical quality criteria to be set by legislative bodies.
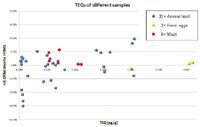
Figure 2. Relative difference in the sum of PCDD/PCDF congener quantitative results (TEQ WHO98 upperbound values) for 40 foodstuff and animal feed samples analyzed by GC-HRMS and GC/MS/MS
COMPOUNDS
- As specified in US and EU legislation
- 7 PCDD congeners
- 10 PCDF congeners
KEY BENEFITS
- Retention-time locked method for ease of chromatographic set-up.
- Capillary flow technology provides concurrent backflush for improved method robustness.
- Excellent linearity and response reproducibility for dioxins in foodstuffs and animal feed over the range of interest.
- Reproducible response even at low fg levels on column.
- Detection down to low pg WHO-TEQ/g.
- Chromatographic results that meet legislated screening requirements for EU methods.
- Mass Hunter software that is very powerful yet easy to master, providing excellent data review capabilities and easy, flexible reporting of data.
* Full analytical details are available in Agilent Technologies publication 5990-6594EN.
Agilent shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this material. Information, descriptions, and specifi cations in this publication are subject to change without notice.
Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.
Using Chromatography to Study Microplastics in Food: An Interview with Jose Bernal
December 16th 2024LCGC International sat down with Jose Bernal to discuss his latest research in using pyrolysis gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (Py-GC–MS) and other chromatographic techniques in studying microplastics in food analysis.
The Use of SPME and GC×GC in Food Analysis: An Interview with Giorgia Purcaro
December 16th 2024LCGC International sat down with Giorgia Purcaro of the University of Liege to discuss the impact that solid-phase microextraction (SPME) and comprehensive multidimensional gas chromatography (GC×GC) is having on food analysis.