Quantification of Purine Alkaloids and Catechins in Green and Black Tea Using Comprehensive 2D-LC
Special Issues
Comprehensive 2D-LC enables the analysis and quantification of purine alkaloids and catechins in green and black tea. As expected, green tea contained higher amounts of the catechins epigallocatechin gallate and epicatechin than black tea.
This application note discusses the comprehensive 2D-LC analysis of green and black tea. The purine alkaloids caffeine and theobromine, as well as the catechins catechin, epicatechin, and epigallocatechin gallate, are quantified.
Tea, produced from the tea plant Camellia sinensis, is one of the most widely consumed beverages worldwide and is characterized by a highly complex composition. Depending on the processing methods of the leaves, three forms of tea are obtained; green tea, oolong, and black tea. The predominant polyphenols in green tea are catechins, whereas in the production of black tea, the monomeric catechins undergo oxidative polymerization (1–4). Quantification of the purine alkaloids caffeine and theobromine, and the tea catechins catechin, epicatechin, and epigallocatechin gallate, enables a comparison of green and black tea.
Experimental Conditions
Comprehensive 2D-LC analysis was achieved with the Agilent 1290 Infinity II 2D-LC Solution. In the first dimension, an Agilent ZORBAX Eclipse Plus C18 column (2.1 × 100 mm, 3.5 µm) was used with a gradient of water and methanol, each with 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid and at a flow rate of 0.1 mL/min. The second dimension separation used an Agilent Poroshell 120 Bonus-RP column (3.0 × 50 mm, 2.7 µm) with shifted gradients of water and acetonitrile, each with 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid, at a flow rate of 2.5 mL/min. Modulation was achieved using the Agilent 2-position/4-port-duo valve, equipped with two 60 µL loops. A modulation time of 21 s was employed. Detection was performed at 280 nm.
Results
Deploying reversed-phase LC in the first and second dimension, a comprehensive 2D-LC method for the analysis of purine alkaloids and catechins in green and black tea was developed. Figure 1a shows that only the two-dimensional setup enabled complete separation of the purine alkaloids and catechins. In the first-dimension separation, caffeine and epigallocatechin gallate coeluted but were resolved in the second-dimension separation. Deploying only the second-dimension separation, catechin, and epicatechin would coelute. The precision of retention times and peak volumes was determined by multiple injection (n = 10) of purine alkaloids and catechins. In the second dimension, the retention time precision was always below 2.5%, and the peak volume precision was always below 1%. Excellent linearity was achieved for all purine alkaloids and catechins. Ten different samples of green and black tea were analyzed, and purine alkaloids and catechins were quantified. Theophylline could not be detected in any of the tea samples.
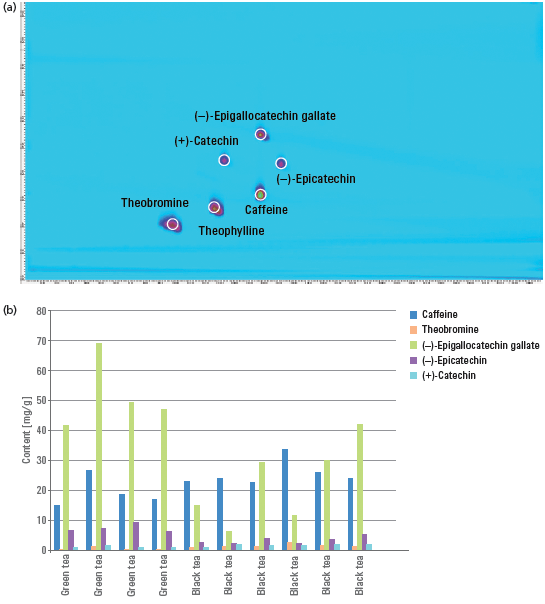
Figure 1: (a) Comprehensive 2D-LC separation of purine alkaloids and catechins; (b) quantification results of purine alkaloids and catechins in green and black tea.
Figure 1b shows the quantification results for purine alkaloids and catechins in green and black tea. As expected, the green tea samples generally contained higher amounts of the catechins epigallocatechin gallate and epicatechin than the black tea samples.
Conclusions
Comprehensive 2D-LC enables the analysis and quantification of purine alkaloids and catechins in green and black tea. As expected, green tea contained higher amounts of the catechins epigallocatechin gallate and epicatechin than black tea.
References
(1) D. Del Rio et al., J. Agric. Food Chem. 52, 2807–2815 (2004).
(2) M.S. El-Shahawi et al., Food Chem. 134, 2268–2275 (2012).
(3) K.M. Kalili and A. de Villiers, J. Sep. Sci. 33, 853–863 (2010).
(4) A.P. Neilson et al., J. Chromatogr. A 1132, 132–140 (2006).

Agilent Technologies, Inc.
5301 Stevens Creek Blvd., Santa Clara, CA 95051
tel. (800) 227-9770
Website: www.agilent.com

A Novel Two-Step Workflow for Extracting Clean Mass Spectra in LC×LC–HRMS Data
March 3rd 2025LCGC International spoke to Paul-Albert Schneide and Oskar Munk Kronik about the development and application of a novel two-step workflow—mass filtering (MF) combined with multivariate curve resolution (MCR)—for extracting clean mass spectra from trace-level compounds in LC×LC–HRMS data.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)













