Market Profile: Flash Chromatography
Flash chromatography has become a popular method of normal-phase separation through purification.
Flash chromatography is a type of preparative liquid chromatography commonly used in the separation of organic compounds. It uses a plastic column filled with some form of solid support, usually silica gel, with the sample to be separated placed on top of this support. The rest of the column is filled with an isocratic or gradient solvent that, with the help of pressure, enables the sample to run through the column and become separated.
Flash chromatography is a type of preparative liquid chromatography commonly used in the separation of organic compounds. It uses a plastic column filled with some form of solid support, usually silica gel, with the sample to be separated placed on top of this support. The rest of the column is filled with an isocratic or gradient solvent that, with the help of pressure, enables the sample to run through the column and become separated.
Flash chromatography has become a popular method of normal-phase separation through purification. Although flash chromatography is typically a low-pressure technique, scientists are using vacuums or pumps at medium pressures to speed the separation process. The columns are packed with a silica adsorbent of defined particle size usually between 30 and 60 mm, although other packings with other particle sizes are also used. Mobile phases with low viscosity require smaller particle sizes.
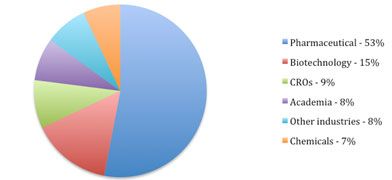
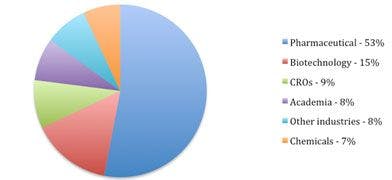
Demand for flash chromatography comes primarily from the pharmaceutical industry accounting for over half of the market. Biotechnology, contract research organization (CRO), academic, and chemical industries complete the top five industries that use flash chromatography. The technique is commonly used in the separation of synthetic organic compounds, which are particularly useful in drug discovery. Flash chromatography systems assist laboratories focusing on combinatorial chemistry to streamline their purification steps.
The foregoing data were extracted and adapted from SDi's recently published report titled Laboratory Sample Preparation Techniques: Breaking the Productivity Bottleneck - Prep Chromatography, Extraction & Concentration. For more information, contact Glenn Cudiamat, VP of Research Services, Strategic Directions International, Inc., 6242 Westchester Parkway, Suite 100, Los Angeles, CA 90045, (310) 641-4982, fax: (310) 641-8851, e-mail: cudiamat@strategic-directions.com
Regulatory Deadlines and Supply Chain Challenges Take Center Stage in Nitrosamine Discussion
April 10th 2025During an LCGC International peer exchange, Aloka Srinivasan, Mayank Bhanti, and Amber Burch discussed the regulatory deadlines and supply chain challenges that come with nitrosamine analysis.
Top Execs from Agilent, Waters, and Bruker Take the Stage at J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference
January 16th 2025The 43rd Annual Healthcare J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference kicked off in San Francisco earlier this week. Here’s what top executives from Agilent, Bruker, and Waters, discussed during the event.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)