Digital Update
ESA Biosciences has archived its most recent webinar called "Is Ion Analysis Bringing You Down?" which was produced to give chromatographers insight into efficient and cost-effective strategies for ion analysis using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The webinar addresses many of the concerns that many chromatographers face with ion analysis and includes presentations and a Q&A session featuring ESA scientist, Dr. Ian Acworth, along with industry experts from Synomics Pharmaceutical Services and Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical.
Ion analysis webinar
ESA Biosciences has archived its most recent webinar called "Is Ion Analysis Bringing You Down?" which was produced to give chromatographers insight into efficient and cost-effective strategies for ion analysis using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The webinar addresses many of the concerns that many chromatographers face with ion analysis and includes presentations and a Q&A session featuring ESA scientist, Dr. Ian Acworth, along with industry experts from Synomics Pharmaceutical Services and Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical.

In today's drug development and manufacturing operations, one of the key analysis steps is the measurement of the amount and type of ion or counter ion present in a particular drug formulation. Currently, the analytical technique most commonly used to analyse ions is ion chromatography (IC). However, to perform these ion measurements with IC requires a dedicated single-use system, according to ESA Biosciences. In addition, IC cannot readily measure anions and cations simultaneously, the company says.
As well as access to a case study which describes practical solutions to overcome real world problems, webinar participants can download all previous presentations for free. They can also learn about the success and accuracy of a method combining an HPLC charged aerosol detector (CAD) with hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) to simplify the analysis of ions. HILIC separates both anions and cations from rather complex samples, while the detector simultaneously identifies these ions, according to the manufacturer.
To access this and other archived webinars for chromatographers go to http://www.esainc.com/news/webinars.
Proteomics platform
Agilent Technologies has launched a new website for proteomics researchers at www.proteomics-lab.com to provide scientists with the latest instrument, software and workflow-related information that the company offers in this field
The site provides overviews of common proteomics challenges including biomarker discovery, protein identification, quantitative proteomics, glycan and glycoprotein analysis, phosphoprotein analysis, and intact protein analysis. It also provides access to recent posters, applications technical notes, videos, events, promotions and information about innovative Agilent products designed to optimize sample preparation and analysis. Ken Miller, Agilent marketing director, LC–MS Division, said the proteomics site would strengthen the company's biodiscovery portfolio.
Software for two-dimensional HPLC
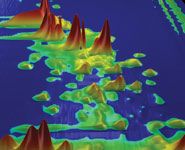
LC×LC Software offers visualization, analysis, and reporting for data from comprehensive two-dimensional (2D) liquid chromatography (LC). This software package includes an extensive suite of automated and interactive tools, developed on the basis of GC Image's GC×GC software and includes two programs: LC Image for visualizing, analysing, and reporting on 2D HPLC data and LC Project for managing and reporting on sequences or batches of 2D HPLC data sets.
LC×LC Software provides interactive, multi-layered visualizations with 3D perspective rendering, 2D pseudocolor images, 1D graphs, and tabular views and can read popular vendor-specific and industry-standard chromatographic, mass spectral, and ultraviolet (UV) file formats, according to the manufacturer. LC×LC Software implements multidimensional, multispectral data processing, including baseline correction, and performs multidimensional peak detection with parallel factor analysis for multivariate peak unmixing. The software performs automated chemical identification and analysis with advanced Smart Templates and the Computer Language for Identifying Chemicals (CLIC). This software has convenient project management tools, including support for calibration tables, and generates reports that can be viewed with a web browser or exported to spreadsheet programs and other software.
LC×LC Software is available for a free trial and GC Image offers special licensing arrangements with collaborating laboratories.
Go to http://www.gcimage.com for further information.
On-line learning technologies
EARL — the Electronic Analytical Reference Library, is an on-line resource for analytical chemists to learn about the principles and practices of techniques used in separation sciences. It has been developed over the past eight years by the analytical chemists and training professionals at Crawford Scientific, with significant contributions by colleagues from industry, academia and instrument vendors.
The library uses modern web-based multimedia techniques to present a wide range of topics in analytical chemistry, including high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) and solid-phase extraction (SPE) at present. More content is continuously being added. Over 2500 pages of online and printable pdf information is arranged in a searchable database for easy access and can be used for "on-demand" learning or as part of pre-programmed courses of study. Students can complete assessments and print certificates to add to training records.

Altering Capillary Gas Chromatography Systems Using Silicon Pneumatic Microvalves
May 5th 2025Many multi-column gas chromatography systems use two-position multi-port switching valves, which can suffer from delays in valve switching. Shimadzu researchers aimed to create a new sampling and switching module for these systems.
Studying Cyclodextrins with UHPLC-MS/MS
May 5th 2025Saba Aslani from the University of Texas at Arlington spoke to LCGC International about a collaborative project with Northwestern University, the University of Hong Kong, and BioTools, Inc., investigating mirror-image cyclodextrins using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC–MS/MS) and vibrational circular dichroism (VCD).

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)










