HPLC Gradient Elution – Baseline Drift
The CHROMacademy technical team was recently posed with the question of the causes of baseline drift in gradient HPLC.
The CHROMacademy technical team was recently posed with the question of the causes of baseline drift in gradient high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (Figure 1).
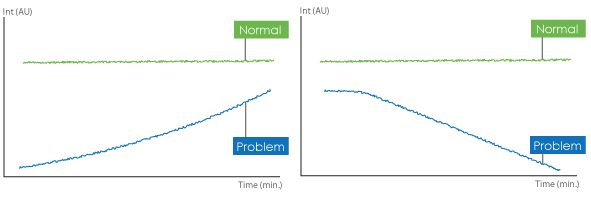
The primary cause of baseline drift in gradient HPLC is due to changes in the refractive index of the eluent. During gradient elution the composition of the eluent will change and, hence, so will its refractive index. This usually manifests itself as a gradual increase in response during the gradient time. To compensate for the change in refractive index properties a reference wavelength should always be set otherwise drifting baselines will occur.
Positive baseline drift is commonly seen in gradient elution and is often caused by differences in the absorbance properties of the A and B solvents. In the case of reversed phase HPLC gradient elution the eluent composition will change from a high percent of A (aqueous) to a high percent B (organic solvent). The common organic solvents used in reversed phase HPLC have a greater UV absorbance (Table 1) than aqueous (water) which results in the rising baseline when monitoring at low wavelengths (~200 nm). The problem of baseline drift caused by the disparity in UV absorbance can be remedied in three ways.
The complete article is available to CHROMacademy Lite and Premier members here >>
CHROMacademy Lite Membership is FREE and it only takes two minutes to register.
With a Lite Membership you are given access to:
∙ This month's webcast & tutorial
∙ Selected eLearning modules
∙ Featured CHROMacademy Content
∙ The CHROMacademy forum
Test drive CHROMacademy and Check out more great content available FREE to our Lite members »
Determining the Effects of ‘Quantitative Marinating’ on Crayfish Meat with HS-GC-IMS
April 30th 2025A novel method called quantitative marinating (QM) was developed to reduce industrial waste during the processing of crayfish meat, with the taste, flavor, and aroma of crayfish meat processed by various techniques investigated. Headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS) was used to determine volatile compounds of meat examined.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)





