On-line SPE-LC of Catecholamines in Urine with Fluorescence Detection
LCGC Asia Pacific
Knauer Application Note
Introduction
Catecholamines are important markers for the diagnosis and management of tumour diseases of the sympathoadrenal system. The major catecholamines are dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine. Urine tests have shown to be applicable to measure the level of catecholamines in the human body. Various separation methods have been used for the clean-up of catecholamines in biological fluids: solvent extraction, adsorption on alumina, ion-exchange and solid-phase extraction of a diphenylboronic acid-catecholamine complex. From the point of simplicity, reproducibility and automation the last method is the most suitable and can be realized by on-line SPE–LC. Diphenylborate forms a negatively charged complex with the diol groups of catecholamines. These complexes which are strongly retained on a polystyrene-divinylbenzene cartridge in alkaline medium (pH 8.5) can be eluted in a second step from the SPE unit directly onto the HPLC column. The separation of catecholamines is performed in isocratic mode by adjusting the pH value in the acidic range.
Experimental
All parts in the fluid path, except the SPE and analytical columns, require passivation with a nitric acid solution. Because of the high buffer content in SPE eluent and mobile phase it is highly recommended that the filter and sieve combinations, the eluent filter and the precolumn be replaced after 250 injections. The first column inlet filter unit should be installed between the autosampler and switching valve of the on-line SPE unit. A second in-line filter unit should be placed on the outlet of the HPLC pump. For quality control of the analytical determinations we recommend using the ClinChek urine controls. These controls are available for the normal range as well as for the pathological range. The injection volume of the calibration and sample solution is 50 µL.
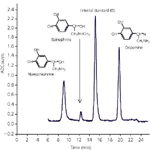
Figure 1: Urine calibrator + 20 µL IS.
Method Parameters
HPLC column: Eurospher 100-5 C18 100 × 4 mm, with precolumn
SPE column: SPE cartridge for catecholamines (Recipe)
HPLC eluent: Mobile phase for catecholamines (Recipe)
SPE eluent: SPE buffer for catecholamines (Recipe)
Flow HPLC eluent: 1.2 mL/min
Injection volume: 50 µ L urine calibrator and sample
Column temp.: 30 °C
System pressure: approx. 50 bar
Detection: Fluorescence: Ex 275 nm, Em 330 nm
Run time: 20 min (incl. regeneration)
SPE Unit 6300

Results and Conclusions
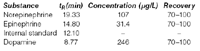
The on-line SPE sample preparation unit 6300 with its HPLC pump in combination with fluorescence detection dramatically streamlines the urine analysis for the determination of catecholamines. Automated sample handling, proprietary column chemistry and sensitive fluorescence detection have been combined. The system requires only a fraction of a typical sample volume. The limit of detection can be calculated with 1 µg/L and the linearity range goes up to 1500 µg/L. Its increased speed, improved accuracy and precision clearly demonstrate the advantage of this hyphenation technique over standard procedures.
References
1. T.G. Rosanjo, T.A. Swift and L.W. Hayes, Clin. Chem., 37(10/2), 1854–1867 (1991).
2. D.J. Wang et al., Chromatographia, 31(3–4), 137–142 (1991).
Wissenschaftliche Gerätebau Dr. Ing. Herbert Knauer GmbH

Hegauer Weg 38, 14163 Berlin, Germany
tel. +49 30 809727 0 fax +49 30 801501 0
E-mail: info@knauer.net Website: www.knauer.net

AOAC International Awarded NIST Grant for Developing Drug Testing Standards
October 31st 2024The grant will be part of a new collaborative scientific initiative to address the need for standards that define the desired performance of lateral flow immunoassay test strips to detect illicit drugs in tablets and powders.
AI and GenAI Applications to Help Optimize Purification and Yield of Antibodies From Plasma
October 31st 2024Deriving antibodies from plasma products involves several steps, typically starting from the collection of plasma and ending with the purification of the desired antibodies. These are: plasma collection; plasma pooling; fractionation; antibody purification; concentration and formulation; quality control; and packaging and storage. This process results in a purified antibody product that can be used for therapeutic purposes, diagnostic tests, or research. Each step is critical to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of the final product. Applications of AI/GenAI in many of these steps can significantly help in the optimization of purification and yield of the desired antibodies. Some specific use-cases are: selecting and optimizing plasma units for optimized plasma pooling; GenAI solution for enterprise search on internal knowledge portal; analysing and optimizing production batch profitability, inventory, yields; monitoring production batch key performance indicators for outlier identification; monitoring production equipment to predict maintenance events; and reducing quality control laboratory testing turnaround time.