Analysis of Active Cannabis Compounds in Edible Food Products: Gummy Bears and Brownies
The Application Notebook
Potency testing in marijuana-infused edibles is a problematic task due to the complexity of the matrices. The concentration of active ingredients in edibles can range from a few ppm to 3.5% (1). In this application, active cannabinoid compounds were extracted from gummy bears (and also brownies, results not shown), followed by HPLC analysis.
Potency testing in marijuana-infused edibles is a problematic task due to the complexity of the matrices. The concentration of active ingredients in edibles can range from a few ppm to 3.5% (1). In this application, active cannabinoid compounds were extracted from gummy bears (and also brownies, results not shown), followed by HPLC analysis.
Experimental
Cannabinoid standards (Cerilliant®) used: cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA), cannabidivarin (CBDV), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabidiol (CBD), tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), cannabinol (CBN), (-)-Δ9âTetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), (-)-Δ8-Tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ8-THC), and (-)-Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid A (THCAA). Even though acidic cannabinoids are not commonly found in edibles, these were included to demonstrate the ability of the HPLC method to resolve them from neutral forms, and the method’s potential for testing cannabis flowers (which contain acidic cannabinoids).
An Ascentis® Express Biphenyl (2.7 µm particles) HPLC column was used for separation of all 11 compounds in under 13 min on a standard pressure HPLC system.
Sample Preparation
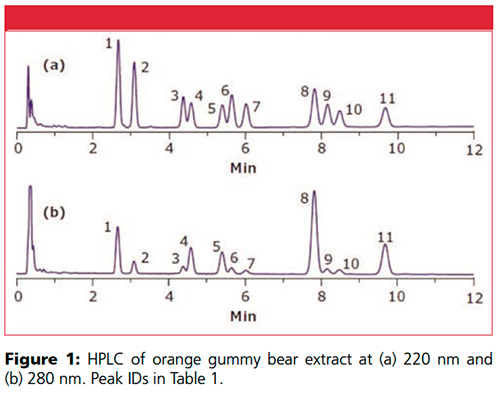
Four different bear colours were tested-orange, yellow, red, and green. One gummy bear, nonspiked, (2.3 g) was dissolved in 20 mL of warm water. This solution was spiked with cannabinoid (45 ppm each), and then transferred to a 50-mL QuEChERS extraction tube. Acetonitrile (10 mL) was added, followed by 1-min shaking. Supel™ QuE nonbuffered salts (55295-U) were added, and the samples were shaken for 5 min followed by 5 min centrifugation (5000 rpm). The supernatant was then injected into the HPLC system (Figure 1).

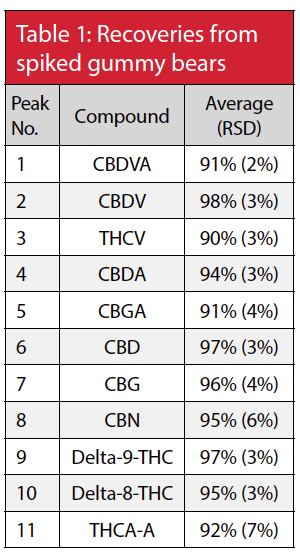
Results
For all bears, detection was at 220 nm, except for CBDVA due to an interference from the orange bear; detection was at 280 nm for that orange bear sample. Excellent recovery values of above 90% were achieved with good accuracies (Table 1).
Column: Ascentis Express Biphenyl, 10 cm × 2.1 mm i.d., 2.7 µm
Mobile phase: (A) 0.1% TFA in water; (B) 0.1% TFA in acetonitrile
Gradient: 47% B, to 50% B in 13 min, to 100% B in 0.1 min, 100% B for 3 min, to 47% B in 0.1 min, at 47% B for 2.5 min
Flow rate: 0.70 mL/min
Temp.: 35 °C
Detector: UV, 220 nm & 280 nm (280 nm)
Injection: 5 µL
Pressure: 340 bar
Instrument: Agilent® 1200, with UV detector
Conclusion
The developed HPLC method showed good resolution and can also be used for analysis of commodities containing acidic cannabinoids; specifically, cannabis flower.
Reference
- http://analytical360.com/m/archived/216628 (accessed July 2016).
Read the full article at SigmaAldrich.com/ar (Issue 4)

Merck
Frankfurter Strasse 250
Darmstadt, 64293, Germany
Website: www.sigmaaldrich.com
